---
comments: true
---
# What is Data Structures and Algorithms?
## Definition of Algorithm
*Algorithm* is a set of instructions or operations to solve a problem (or a set of problems) in a finite amount of time. Algorithms have the following characteristics:
- The problem is clear, and the input and output definitions are clear.
- Deterministic, that is, the same input will always produce the same output.
- Feasible, that is, it can be completed in a finite number of steps, a finite amount of time, and a finite amount of memory space.
- Independent of programming languages, in other words, it can be implemented in multiple languages.
## Definition of Data Structure
*Data Structure* is a way of organizing and storing data in a computer. In order to improve the performance of data storage and operation, the design principles of data structures are:
- Occupying as little space as possible, saving computer memory.
- Data operations should be as fast as possible, including data access, addition, deletion, update, etc.
- Provide concise data representation and logical information to facilitate efficient operation by algorithms.
Data structure design is a process full of compromises, this means that if you get an advantage in one aspect, you will have to make a compromise in another aspect. For example, linked lists are more convenient for data addition and deletion than arrays, but they sacrifice the speed of data access; graphs provide more logical information than linked lists, but occupy more memory space.
## Relationship between Data Structures and Algorithms
*Data Structures* and *Algorithms* are highly related and tightly integrated, which are shown in the following:
- Data structures are the foundation of algorithms. Data structures provide structured data storage and corresponding methods for manipulating data.
- Algorithms are the stage for data structures to show their advantages. Data structures only store information, and only with algorithms can they solve specific problems.
- Algorithms have corresponding optimal data structures. Given an algorithm, it can be implemented based on different data structures, and the final execution efficiency may vary greatly.
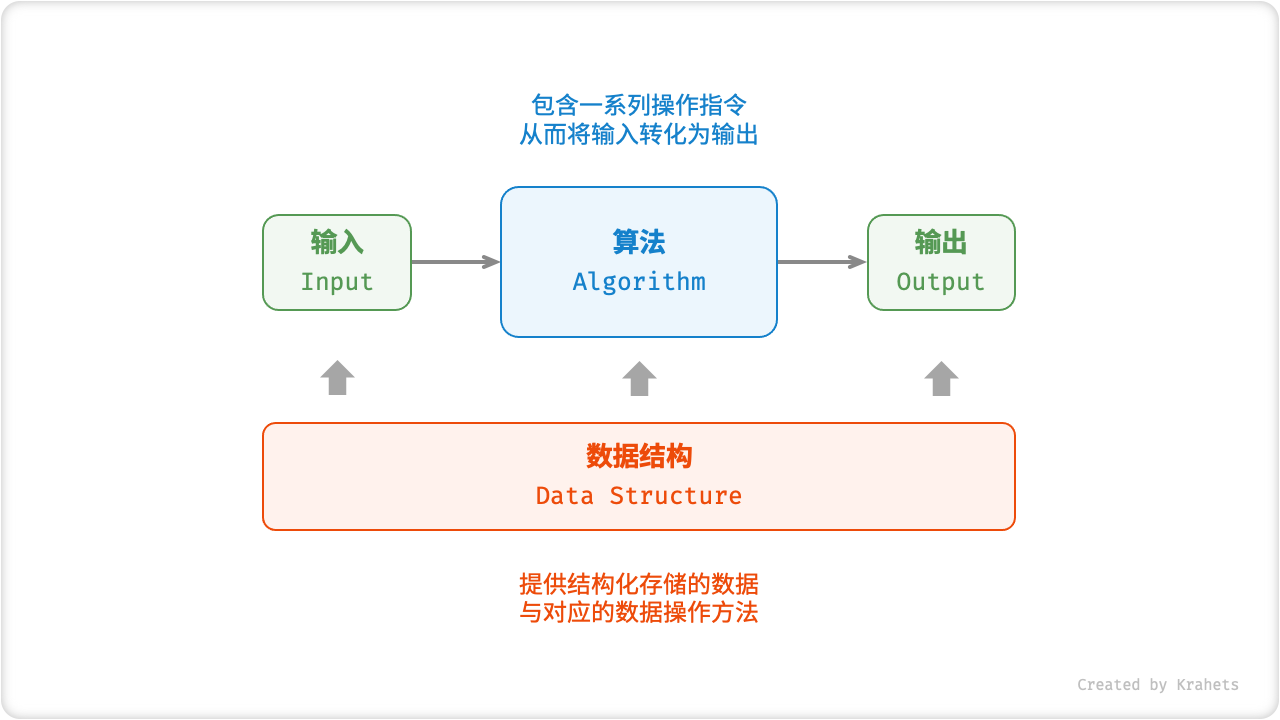
Fig. Relationship between data structures and algorithms
If we compare *Data Structures and Algorithms* to *LEGO*, we can get the corresponding relationship shown in the following table.
| Data Structures & Algorithms | LEGO |
| ------------------------- | -------------------------------------- |
| Input data | LEGO blocks |
| Data structure | The way blocks piece together (including size, shape, connection interface, etc.) |
| Algorithm | The steps to piece all the blocks together to get the desired model |
| Output data | A LEGO model |
!!! tip "A conventional abbreviation"
In discussions, we usually abbreviate *Data Structures and Algorithms* as *Algorithms*. For example, the algorithm problems on LeetCode, actually involve both data structures and algorithms.